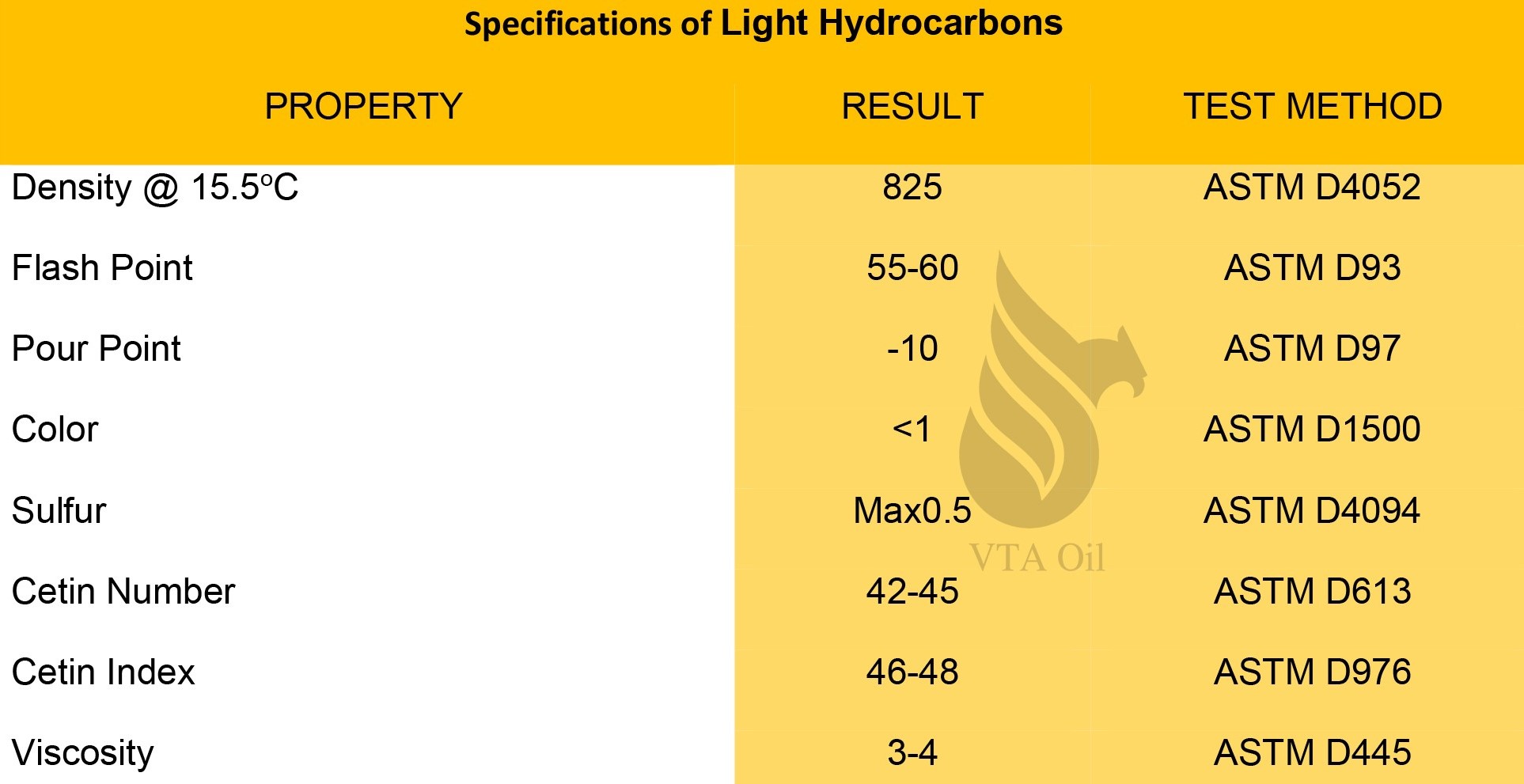
Light Hydrocarbons
are a group of hydrocarbon compounds that consist of relatively small molecules with low molecular weights. They are primarily derived from crude oil or natural gas during refining and processing. These hydrocarbons are characterized by their volatility, low boiling points, and gaseous or light liquid nature at ambient conditions.
Types of Light Hydrocarbons:
1. Methane (CH₄):
• The simplest hydrocarbon.
• Major component of natural gas.
• Used as a fuel and feedstock in chemical industries.
2. Ethane (C₂H₆):
• Found in natural gas and used as a feedstock for ethylene production, a key material in plastics.
3. Propane (C₃H₈):
• A liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
• Used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and as a petrochemical feedstock.
4. Butane (C₄H₁₀):
• Another LPG component.
• Used as fuel, refrigerant, and in the production of butadiene for synthetic rubber.
5. Pentanes (C₅H₁₂):
• Light liquid hydrocarbons.
• Found in natural gas liquids (NGLs).
• Used as a solvent and in gasoline blending.
Sources of Light Hydrocarbons:
1. Natural Gas Processing:
• Raw natural gas contains methane, ethane, propane, and heavier hydrocarbons. Processing separates these into usable components.
2. Crude Oil Refining:
• Light hydrocarbons are produced during distillation and cracking processes in oil refineries.
3. Petrochemical Industry:
• Feedstock for producing olefins (ethylene, propylene) and aromatics.
Applications of Light Hydrocarbons:
1. Energy Source:
• Methane, propane, and butane are commonly used as fuels.
2. Petrochemical Feedstock:
• Ethane and propane are critical in the production of plastics, solvents, and other chemicals.
3. Refrigerants:
• Propane and butane are used as eco-friendly refrigerants.
4. Solvents and Blending Agents:
• Pentane and other light hydrocarbons are used in gasoline blending and industrial solvents.
In summary, light hydrocarbons are essential building blocks in energy production and the petrochemical industry. Their small molecular size and versatility make them fundamental in modern fuel and material production processes.